Grafana Setup and Prometheus Integration as a Data Source
1-) Grafana Setup
Persistent Storage Configuration
Since Grafana's data will be stored on a node in a Kubernetes cluster, PersistentVolume (PV) and PersistentVolumeClaim (PVC) definitions are required. This configuration allows Grafana to protect its data in case of shutdown or restart.
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: grafana-pv
namespace: monitoring
spec:
capacity:
storage: 1Gi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
hostPath:
path: /mnt/data/grafana
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: grafana-pvc
namespace: monitoring
spec
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1GiThe PersistentVolume (PV) and PersistentVolumeClaim (PVC) configuration above allows Grafana to store its data on a specific node. However, the hostPath used here is dependent on the local file system of the specific node where Grafana is running.
Therefore:
- If Grafana pods are moved to a different node, they will lose their data unless they have the same hostPath directory on the new node.
- To guarantee that pods always run on the same node, it is necessary to pin pods to specific nodes using nodeAffinity or nodeSelector.
Alternatively, NFS, Ceph, Longhorn or a cloud-based storage solution can be used to store data in a node-independent manner.
Grafana Secret Configuration
The username and password to be used in the Grafana interface are stored in the following secret.
// Set the password and passphrase of the admin user who will enter the Grafana interface.
GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_USER=admin
GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_PASSWORD=<YOUR_GRAFANA_PASSWORD>
echo -n ${GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_USER} | base64
//We will replace this output with the <ENCODED_GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_USER> variable in the next step
echo -n ${GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_PASSWORD} | base64
//We will replace this output with the <ENCODED_GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_PASSWORD> variable in the next stepapiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: grafana-secrets
namespace: monitoring
type: Opaque
data:
GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_USER: <ENCODED_GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_USER>
GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_PASSWORD: <ENCODED_GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_PASSWORD>Grafana Deployment Configuration
Modify the Grafana Deployment YAML file below to suit your systems and install it on your Kubernetes Cluster.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: grafana
name: grafana
namespace: monitoring
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: grafana
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: grafana
spec:
initContainers:
- name: init-permissions
image: busybox
command: ["sh", "-c", "chown -R 472:472 /var/lib/grafana"]
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /var/lib/grafana
name: grafana-storage
containers:
- name: grafana
image: grafana/grafana:11.6.1
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- containerPort: 3000
name: http-grafana
protocol: TCP
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /api/health
port: 3000
scheme: HTTP
initialDelaySeconds: 10
periodSeconds: 30
successThreshold: 1
timeoutSeconds: 5
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /api/health
port: 3000
scheme: HTTP
initialDelaySeconds: 30
periodSeconds: 10
successThreshold: 1
timeoutSeconds: 5
resources:
requests:
cpu: 256m
memory: 256Mi
envFrom:
- secretRef:
name: grafana-secrets
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /var/lib/grafana
name: grafana-storage
volumes:
- name: grafana-storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: grafana-pvcKubernetes Service is created for Grafana.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: grafana
namespace: monitoring
labels:
app: grafana
spec:
ports:
- name: http
port: 3000
nodePort: 32181
selector:
app: grafana
type: NodePortWhen Grafana is deployed on Kubernetes, it creates a Kubernetes service named grafana and of type NodePort. This service is required for access to Grafana from outside Kubernetes. However, instead of this service, you can use Ingress or whatever structure you use for the connection method in your organization.
2) Setting Prometheus as Data Source on Grafana
1. Sign in to Grafana
2. Click on the Data Source tab in the Left Menu and select Add new data source.

3. Select Prometheus as data source.
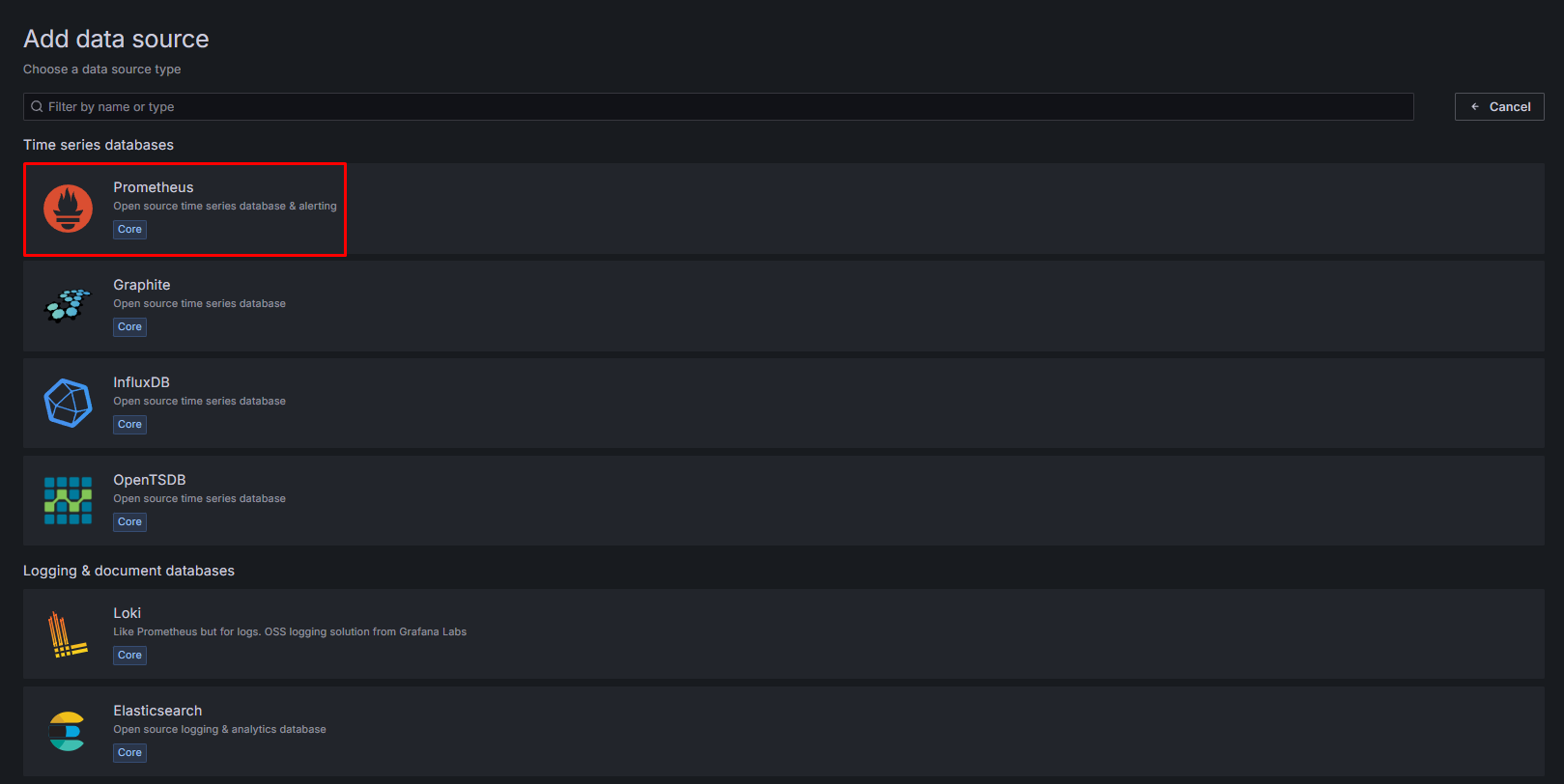
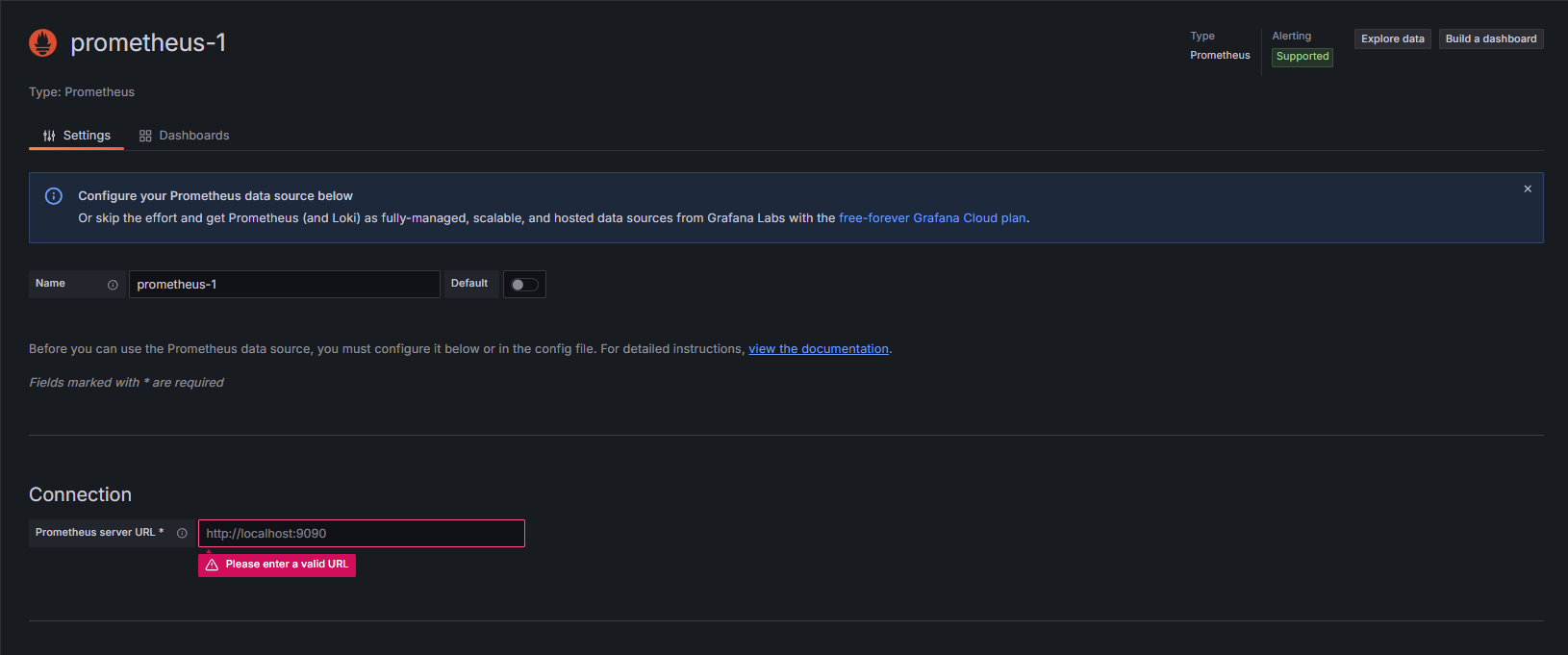
4. Enter and save the Prometheus Connection url and other required settings.
5. Click on the Dashboard tab from the Left Menu and select new dashboard.
6. Create a new dashboard and select prometheus as data source.