API Integration Installation
This document describes the installation of Apinizer Integration.
1) Introduction
API integration provides the ability to create workflows by enabling one or more endpoints to be fluidly connected together.
2) Pre-installation Steps
Before starting the installation of Apinizer API Integration, the following should be noted:
- API Manager must be installed. For API Manager Installation, please review the Apinizer Installation and Settings document.
- API Integration must be included in your license key.
3) Installation Steps
API Integration Installation is done in two ways.
- If Kubernetes management is done via Apinizer, you can set up API Integration via API Manager.
- If Kubernetes management is not done via Apinizer, a manual installation can be done on Kubernetes and then a connection can be established with API Manager.
3.1) Installing API Integration via API Manager
3.1.1) If API Integration Setup will be done via API Manager
For API Integration setup via API Manager, the following section must be active in the General Settings menu.

In API Manager, go to Administration → Server Management → Kubernetes Resources page. Enable API Integration from the Deployment & Pods tab. Complete the setup by making the necessary definitions.

in the dialog that opens, define the mandatory fields appropriate for your organization.
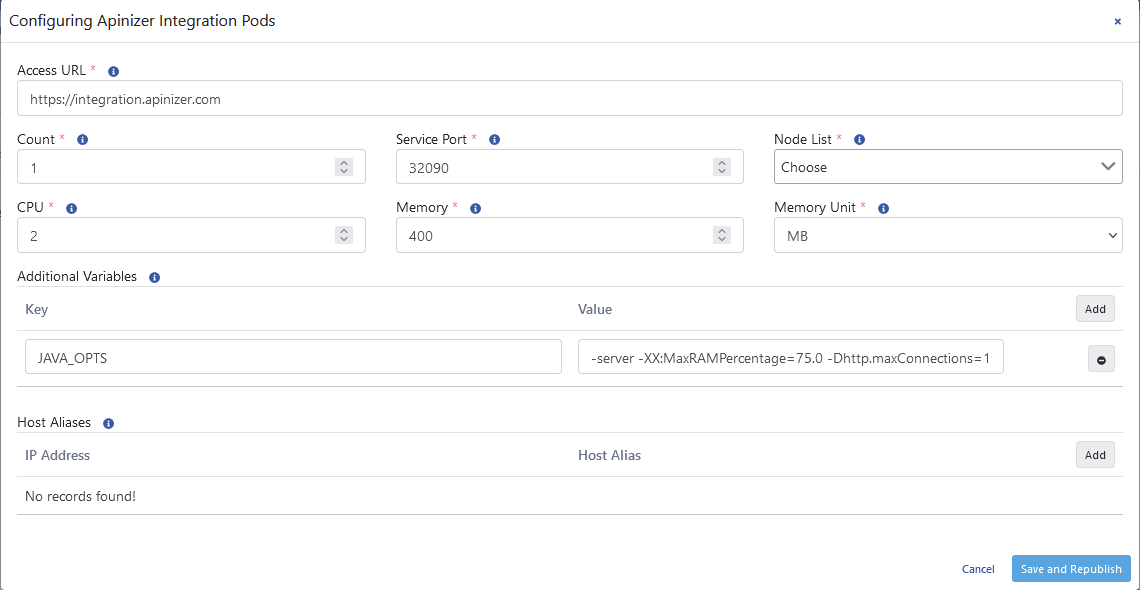
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Access URL | API Integration access address. Example address: http://<Integration_Access_Address>port |
| Count | The number of Gateway engines is equivalent to the replicaSet in Kubernetes Cluster. |
Service Port | Gateway engine access port is equivalent to NodePort in Kubernetes Cluster. |
Node List | Sets which Kubernetes Worker servers the pods will run on. Edit the NodeAffinity setting in Kubernetes. |
CPU | This is the maximum number of CPU cores that the pod will use. |
Memory | The maximum memory value that the pod will use. |
Memory Unit | The unit of value required for memory is selected; MB, GB. |
Additional Variables | Default and optional variables and their values are defined to be run in the pod. Default variables cannot be deleted, only their values can be edited. |
Host Aliases | IP addresses on the network can sometimes be placed behind host names. If these are not defined in the nameserver or host file, or if Apinizer cannot resolve them in some way, a Host Alias must be defined for worker pods to resolve these names. |
After completing the above steps and ensuring that the Pods belonging to API Integration on Kubernetes are ready, you can start using it from the Project → Development → API Integrator → Task Flows menu.
The following warning should be taken into account when configuring the Java Options setting in the Additional variables area:
When-Xmx and -Xms parameters are used, automatic heap sizing is disabled.
Apinizer sets the JVM Heap values to use 75% of the memory given to the container since it is running inside the container.
UseContainerSupport is active by default.
The old flags -XX: {Min|Max} RAMFraction are now deprecated. There is a new flag -XX: MaxRAMPercentage which takes a value between 0.0 and 100.0 and defaults to 75.0. Therefore, if there is a 1 GB memory limit, the JVM heap is limited to ~750 MB by default.
Click for detailed information.
3.1.2) If API Integration Setup will not be done through API Manager
Create a namespace for the integration.
kubectl create ns apinizer-integrationTake the 'mongo-db-credentials' secret from the Apinizer namespace and add it to the apinizer-integration namespace.
kubectl get secret mongo-db-credentials -n apinizer -o yaml | sed 's/namespace: apinizer/namespace: apinizer-integration/' | kubectl create -f -Create the Deployment yaml for Integration.
vi integration-deployment.yamlapiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: integration
namespace: apinizer-integration
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: integration
version: v1
strategy:
rollingUpdate:
maxSurge: 1
maxUnavailable: 75%
type: RollingUpdate
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: integration
version: v1
spec:
containers:
- env:
- name: JAVA_OPTS
value: -server -XX:MaxRAMPercentage=75.0 -Dlog4j.formatMsgNoLookups=true
- name: SPRING_DATA_MONGODB_URI
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
key: dbUrl
name: mongo-db-credentials
- name: SPRING_DATA_MONGODB_DATABASE
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
key: dbName
name: mongo-db-credentials
- name: SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE
value: prod
image: apinizercloud/integration:<APINIZER_VERSION>
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
livenessProbe:
failureThreshold: 3
httpGet:
path: /apinizer/management/health
port: 8092
scheme: HTTP
initialDelaySeconds: 120
periodSeconds: 30
successThreshold: 1
timeoutSeconds: 30
name: integration
ports:
- containerPort: 8092
protocol: TCP
readinessProbe:
failureThreshold: 3
httpGet:
path: /apinizer/management/health
port: 8092
scheme: HTTP
initialDelaySeconds: 120
periodSeconds: 30
successThreshold: 1
timeoutSeconds: 30
resources:
limits:
cpu: "1"
memory: 1024Mi
startupProbe:
failureThreshold: 3
httpGet:
path: /apinizer/management/health
port: 8092
scheme: HTTP
initialDelaySeconds: 91
periodSeconds: 30
successThreshold: 1
timeoutSeconds: 30
hostAliases:
- ip: "<IP_ADDRESS>"
hostnames:
- "<DNS_ADDRESS_1>"
- "<DNS_ADDRESS_2>"kubectl apply -f integration-deployment.yamlTo see the status of the created Pod, you can use the following Kubectl command:
kubectl get pods -n apinizer-integration 
If Ingress will not be used in service creation, the definition is created with the NodePort type and the pod's non-cluster access is set.
vi apinizer-integration-service.yamlapiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
name: integration
namespace: apinizer-integration
spec:
ports:
- nodePort: 32090
port: 8092
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 8092
selector:
app: integration
type: NodePortkubectl apply -f apinizer-integration-service.yamlConnecting the Created API Integration Application to the API Management Console
In API Manager, go to System Settings → General Settings. Enable API Integration in the “Define API Integration (Task Flow) Module information.” section. Complete the installation by making the necessary definitions.
