Apinizer Healthcheck and Version Addresses
This document explains how to check the health status and version information of the main modules (Manager, Worker, Cache, Integration, and Portal) in your Apinizer deployment. These checks are critical for verifying that your system is functioning properly, identifying potential issues early, and guiding you through troubleshooting processes.
General Approach
We can perform health checks and version checks on Apinizer modules using two main methods:
Inside of Kubernetes:
This is done by sending requests via internal service names using the curl command from a pod within the cluster. This method is ideal for diagnosing cluster-internal communication problems.
Outside of Kubernetes:
If your modules are exposed externally (NodePort, LoadBalancer, Ingress), requests are made directly to the access URLs from your local machine or server. This method is useful for testing general accessibility and external integrations.
Inside of Kubernetes:
This method is used to check the availability and status of Apinizer modules within the Kubernetes cluster via the internal network.
Pods and Their Conditions Are Detected
All Pods in the cluster and their statuses are checked. This shows which Pods are running and in which Namespaces they are located.
kubectl get pods -AThis will output all pods in your system. In this example, all pods are running healthily:
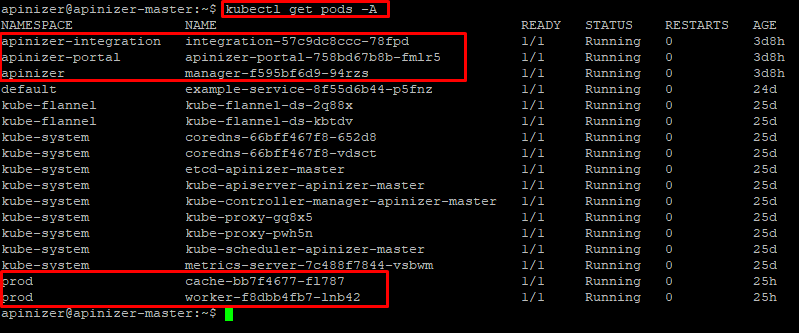
In this output, you can see that all Pods are in Running status and the READY column is 1/1, which indicates that they are healthy.
Service Information Detected
Information about the services that enable communication between pods is identified. This allows you to find service names, related namespaces, and internal ports.
kubectl get svc -AExample output:

As shown in this example, the Apinizer Namespaces and Ports are listed in the table below.
| Module | Service Name | Service Type | Namespace | Internal Port | External Port |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manager | manager | NodePort | apinizer | 8080 | 32080 |
| Worker | worker-http-service | NodePort | prod | 8091 | 30080 |
| Cache | cache-http-service | ClusterIp | prod | 8090 | - |
| Integration | integration-http-service | NodePort | apinizer-integration | 8092 | 30088 |
| Portal | apinizer-portal-service | NodePort | apinizer-portal | 8080 | 32090 |
Based on this information, URLs can be created in the template below and checked by curling to these URLs from any pod within Kubernetes.
http://<SERVICE_NAME>.<NAMESPACE>.svc.cluster.local:<SERVICE_INTERNAL_PORT>/apinizer/management/healthManager:
kubectl exec -it <any_pod_name> -n <namespace> -- curl -X GET http://manager.apinizer.svc.cluster.local:8080/apinizer/management/healthTo check the version information:
kubectl exec -it <any_pod_name> -n <namespace> -- curl -X GET http://manager.apinizer.svc.cluster.local:8080/apinizer/management/versionWorker:
kubectl exec -it <any_pod_name> -n <namespace> -- curl -X GET http://worker-http-service.prod.svc.cluster.local:8091/apinizer/management/healthTo check the version information:
kubectl exec -it <any_pod_name> -n <namespace> -- curl -X GET http://worker-http-service.prod.svc.cluster.local:8091/apinizer/management/version
Cache:
kubectl exec -it <any_pod_name> -n <namespace> -- curl -X GET http://cache-http-service.prod.svc.cluster.local:8090/apinizer/management/healthTo check the version information:
kubectl exec -it <any_pod_name> -n <namespace> -- curl -X GET http://cache-http-service.prod.svc.cluster.local:8090/apinizer/management/versionIntegration:
kubectl exec -it <any_pod_name> -n <namespace> -- curl -X GET http://integration-http-service.apinizer-integration.svc.cluster.local:8092/apinizer/management/healthTo check the version information:
kubectl exec -it <any_pod_name> -n <namespace> -- curl -X GET http://integration-http-service.apinizer-integration.svc.cluster.local:8092/apinizer/management/versionPortal:
kubectl exec -it <any_pod_name> -n <namespace> -- curl -X GET http://apinizer-portal-service.apinizer-portal.svc.cluster.local:8080/apinizer/management/healthTo check the version information:
kubectl exec -it <any_pod_name> -n <namespace> -- curl -X GET http://apinizer-portal-service.apinizer-portal.svc.cluster.local:8080/apinizer/management/versionOutside of Kubernetes: (With external access URLs)
If your Apinizer modules are configured to be accessible from outside Kubernetes (e.g., NodePort, LoadBalancer type services, or through an Ingress Controller), you can send requests directly from an HTTP client such as Postman or from your local terminal using curl.

Services exposed externally with the NodePort service type of Apinizer modules can be accessed from any client via Kubernetes Node IP addresses and Node Ports. The following table provides details about Apinizer services:
| Module | Service Name | Service Type | Namespace | Internal Port | External Port |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manager | manager | NodePort | apinizer | 8080 | 32080 |
| Worker | worker-http-service | NodePort | prod | 8091 | 30080 |
| Cache | cache-http-service | ClusterIp | prod | 8090 | - |
| Integration | integration-http-service | NodePort | apinizer-integration | 8092 | 30088 |
| Portal | apinizer-portal-service | NodePort | apinizer-portal | 8080 | 32090 |
Manager:
curl "http://<MANAGER_ACCESS_URL>/apinizer/management/health"To check the version information:
curl "http://<MANAGER_ACCESS_URL>/apinizer/management/version"Worker:
curl "http://<WORKER_ACCESS_URL>/apinizer/management/health"To check the version information:
curl "http://<WORKER_ACCESS_URL>/apinizer/management/version"Integration:
curl "http://<INTEGRATION_ACCESS_URL>/apinizer/management/health"To check the version information:
curl "http://<INTEGRATION_ACCESS_URL>/apinizer/management/version"Portal:
curl "http://<PORTAL_ACCESS_URL>/apinizer/management/health"To check the version information:
curl "http://<PORTAL_ACCESS_URL>/apinizer/management/version"Accessing Cache from Outside Kubernetes
The cache module is not exposed externally by default in installations (ClusterIP service type). Therefore, if you want to perform health checks and version checks directly from outside Kubernetes, you must configure the Cache service's port 8090 to be accessible externally.