Apinizer Multi-Region Installation
This document explains step by step how Apinizer works on a multi-region Kubernetes architecture.
Here, only the operations that need to be done specifically for Apinizer are explained. Details about the Kubernetes cluster and Apinizer installation are not within the scope of this document and are provided in a separate document.
For Kubernetes cluster installation, you can refer to the Kubernetes Installation page.
For Apinizer installation, you can refer to the Apinizer Installation page.
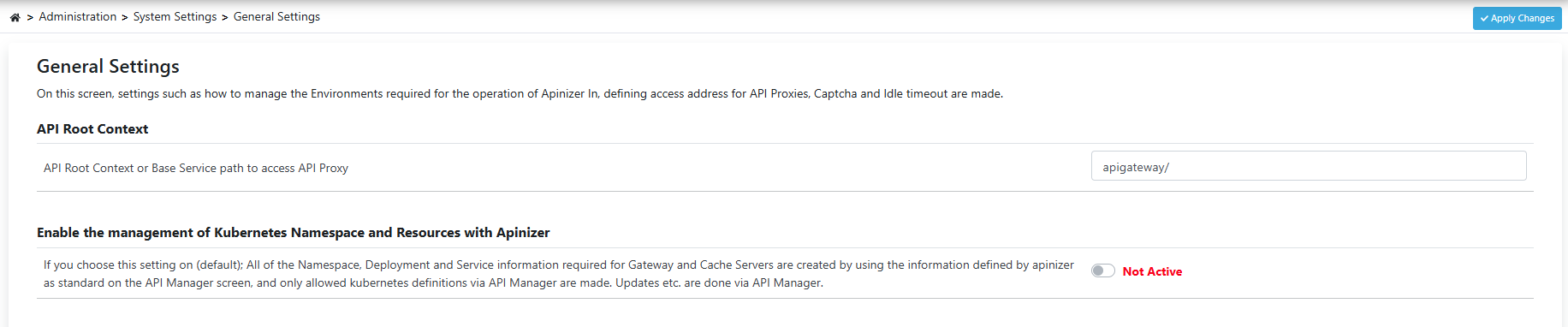
1) Disabling Kubernetes Namespace and Resource Management Feature
To disable the management of Kubernetes namespace and resources via Apinizer, you can follow the steps below:
- Go to the Administration menu.
- Then open the System Settings → General Settings tab.
- Disable the option “Enable the management of Kubernetes Namespace and Resources with Apinizer”.
- Save the changes.
2) Creating an Environment
In this step you can add a new environment or define multiple clusters to an existing environment.
As an example, let's add the new cluster we created in a different region to the scope of an existing environment named prod.
Administration > Server Management > Gateway Environments page opens.
From this screen, you can define Apinizer Worker and Cache components running in different clusters:
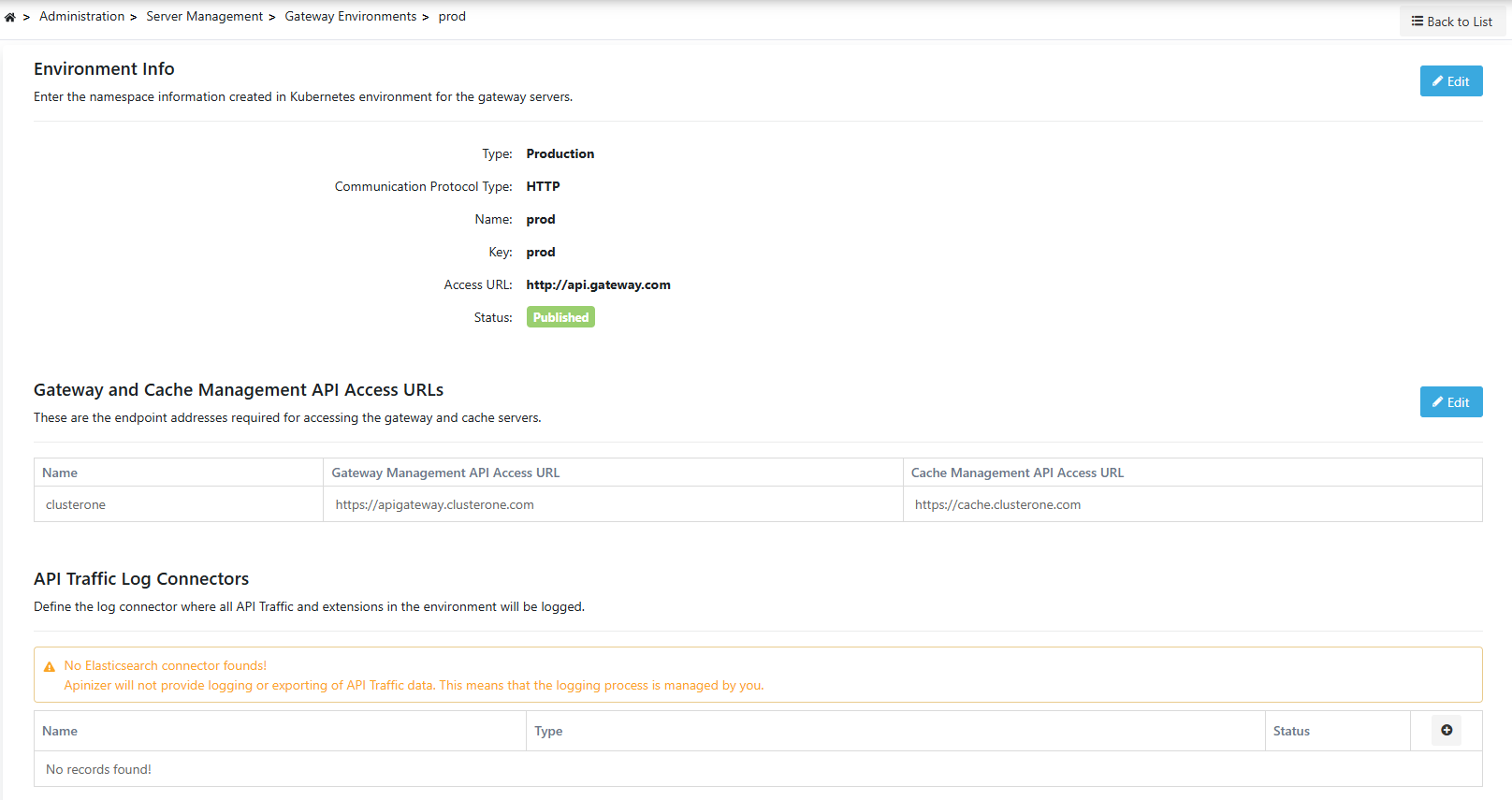
In the Gateway and Cache Management API Access URLs section, management API access information for the Gateway and Cache components of a newly added cluster is defined:
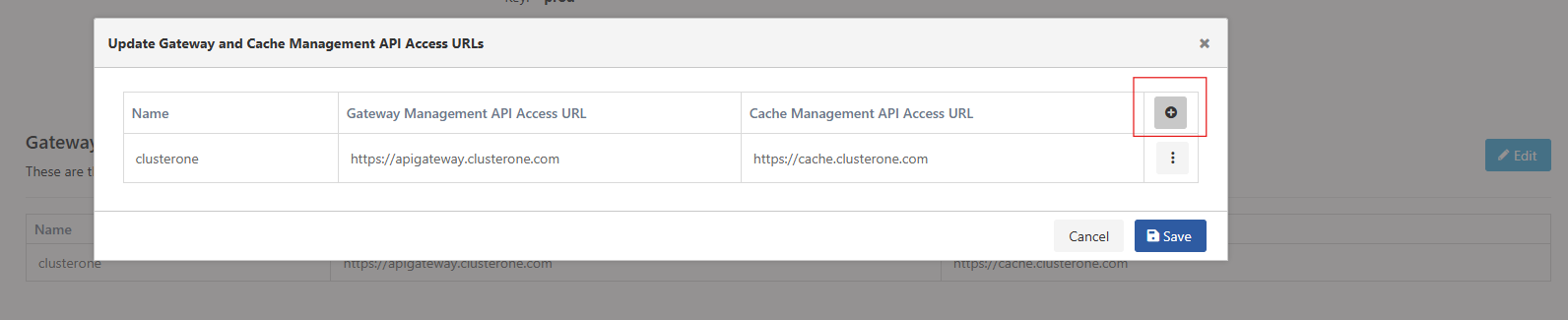
In this step, accessible Gateway and Cache addresses are entered for each cluster.
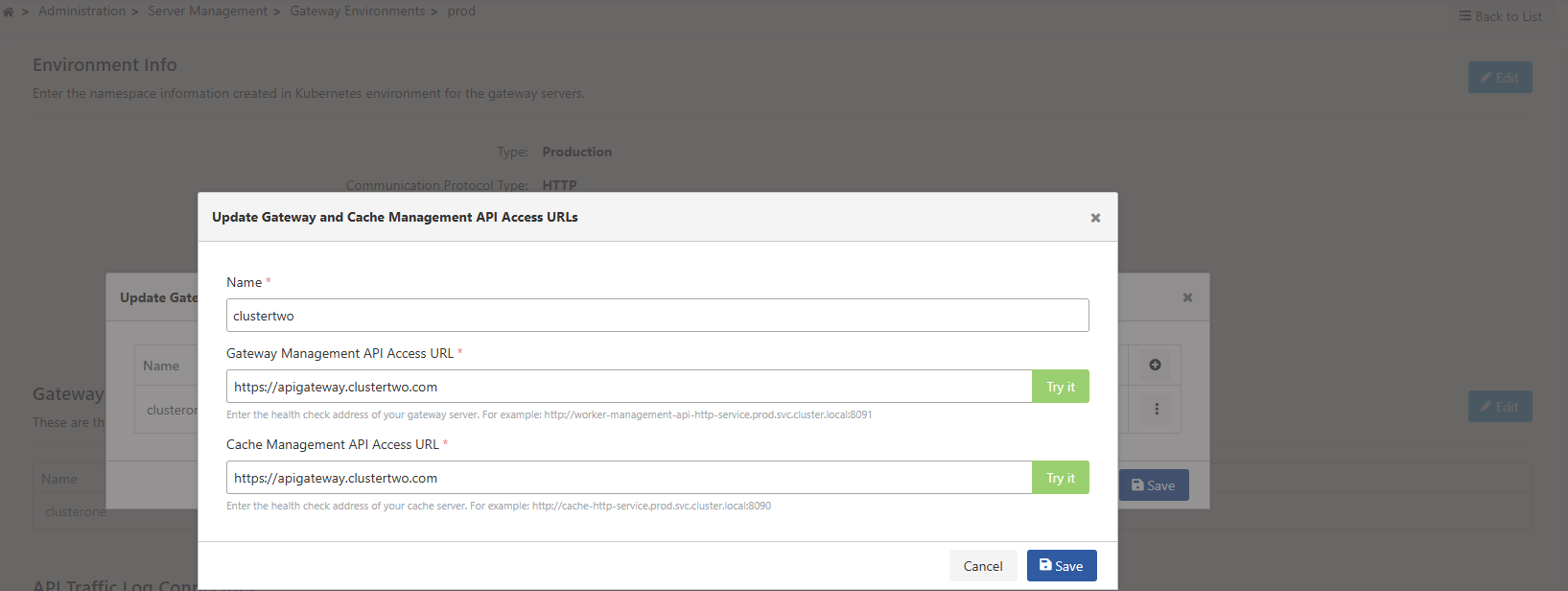
You can test that access is provided by using the "Try it" button.
3) Management with YAML
When the “Enable the management of Kubernetes Namespace and Resources with Apinizer” setting is disabled in the Apinizer interface, Apinizer will no longer automatically create or update namespaces and resources on Kubernetes.
In this case:
- The management of Kubernetes resources (Deployment, Service, Secret, Role, etc.) must be performed manually via YAML files.
- This method provides more flexibility and control in multiple cluster structures.
Cache Matching in Multiple Cluster Environments
In multiple Kubernetes clusters, each Apinizer Worker component needs to know which Cache component to connect to.
This mapping is achieved through a special environment variable to be defined to the Worker pods.
The following environment variable must be added to each Worker Deployment definition:
spec:
containers:
env:
- name: environmentClusterName
value: <NAME>Çok Önemli
- <NAME> is the name representing the cluster where the Cache to which the Worker will connect is located.
- This name must be exactly the same as the cluster name defined under Gateway Environments in the Apinizer interface.
- The Worker component in each cluster communicates only with the Cache component in its own region.