Environment Variables
Environment Variables is a feature in the Apinizer API Management Platform that allows you to centrally manage configuration information that requires different values in different environments (Development, Test, Production). This feature enables the same API Proxy configuration to dynamically use different values such as backend addresses, database connection information, and API keys in different environments.
How It Works
1. Definition Phase
Environment variables are defined at the project level and can be of two types:
- Global (All Environments): Uses the same value in all environments
- Environment-Specific: Different values can be defined for each environment
2. Usage Phase
Environment variables are used in configuration fields in the format ${variableName}:
- Example 1: ${BACKEND_URL} for the backend address
- Example 2: jdbc:mysql://${DB_HOST}:${DB_PORT}/${DB_NAME} for the database connection string
- Example 3: For the API key, use ${API_KEY}
3. Runtime Resolution
When the API Proxy is running (runtime):
- Expressions in the format ${variableName} in the configuration are detected
- The variable value for the relevant environment is retrieved
- Secret values are automatically decrypted
- The variable name is replaced with the actual value
- The process continues with the actual value
Example Scenario:
- Development Environment: BACKEND_URL = dev-api.example.com
- Production Environment: BACKEND_URL = api.example.com
- In configuration: ${BACKEND_URL}
- At runtime in Development: dev-api.example.com
- At runtime in Production: api.example.com
Creating an Environment Variable (Create)
The visual containing the steps for creating an environment variable is provided below:
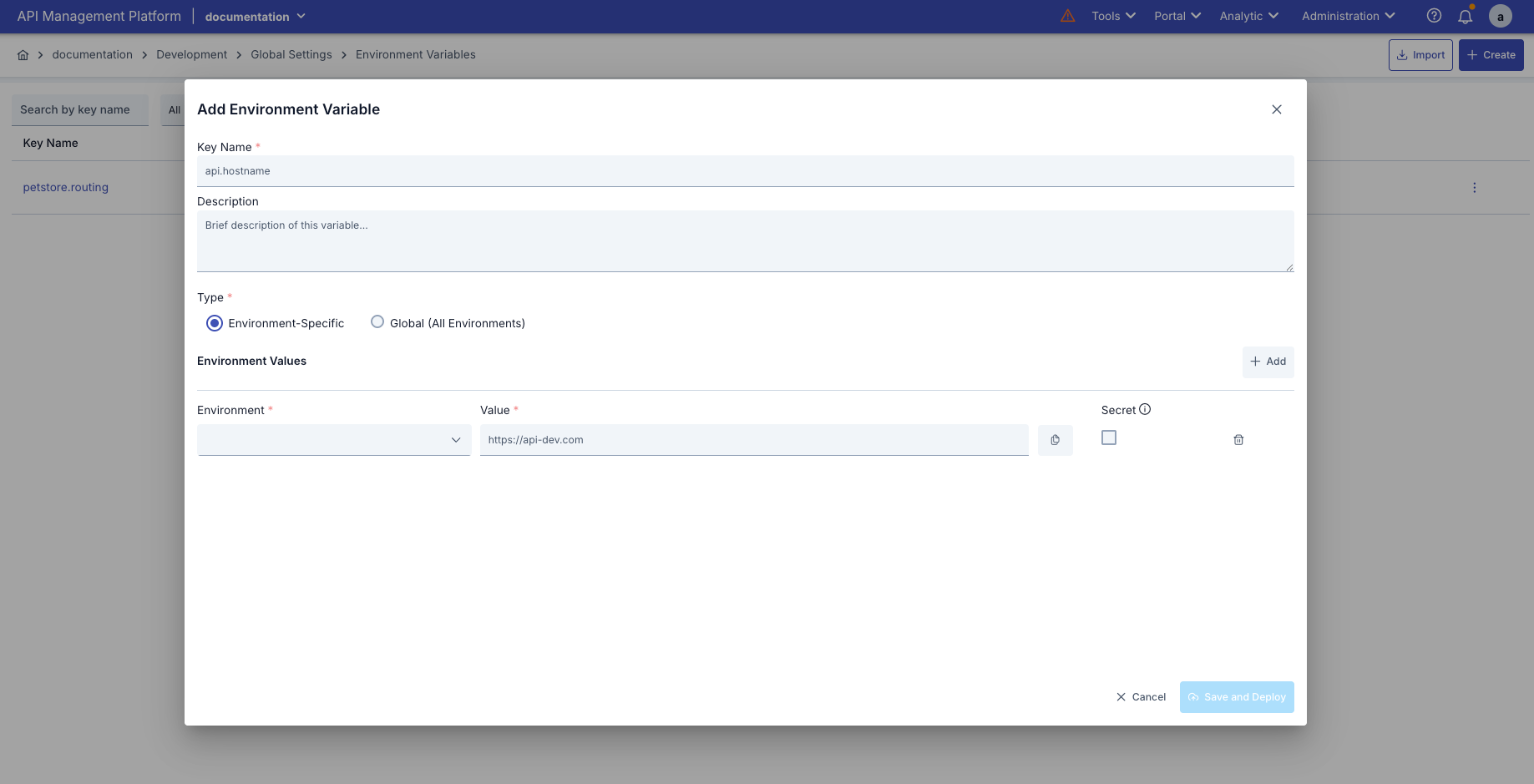
The configurations for creating environment variables are explained step by step in the table below:
| Step | Function |
|---|---|
Step 1: Adding a New Environment Variable |
|
Step 2: Enter Basic Information | Key Name (Variable Name):
Description:
|
Step 3: Selecting the Type | Environment-Specific:
Global (All Environments):
The type selection can only be made when creating a new record. The type of existing records cannot be changed. |
Step 4: Value Definition | Environment-Specific Variables:
For Global Variables:
|
Step 5: Saving and Deployment |
|
Once values marked as secret are saved, they cannot be viewed again.
Environment Variable Editing (Edit)
Opening the Editing Modal
The editing modal can be opened in the following ways:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Click from the List | Click on the environment variable name |
| Select from the Menu | Select “Edit” from the menu at the end of the line |
Differences in the Modal Settings
| Feature | New Entry | Edit |
|---|---|---|
| Modal Header | “Add Environment Variable” | "Edit Environment Variable" |
| Type Selection | Active (editable) | Inactive (non-editable) |
| Secret Values | Visible normally | Visible masked (************) |
| Secret Checkbox | Active | Passive for saved secrets |
Use of Environment Variables
Environment variables can be used in various configuration areas within the Apinizer API Manager platform. This section details how environment variables can be used, in which configurations they can be used, and provides practical examples.
Usage Format
Environment variables are referenced using a special format in configuration files.
Format Structure
| Format | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
${variableName} | Basic usage format | ${BACKEND_URL} |
text${variableName} | Merge with text | https://${API_HOST} |
${variableName}text | Merge with text | ${API_PORT}/api |
text${variable1}text${variable2} | Multiple variables | jdbc:mysql://${DB_HOST}:${DB_PORT}/${DB_NAME} |
Format Rules
| Rule | Description |
|---|---|
| Start Character | Must begin with ${ |
| End Character | Must end with } |
| Variable Name | The variable name appears in the middle (without spaces) |
| Uppercase/Lowercase | Variable names are case-sensitive |
| Special Characters | The variable name can contain periods (.) and underscores (_) |
Usage Locations
Environment variables can be used in various configuration areas on the Apinizer platform. However, the Environment Variable Selection Dialog is only available in certain areas.
1. API Proxy - Routing
Usage Area: Upstream Routing addresses
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Location | API Proxy > Upstream/Routing Tab > Define Address(es) |
| Field | Backend API address input field |
| Usage | Environment-based routing for backend API addresses |
| Access | By clicking the list icon button to the right of the address input field |
2. Database Connection
Usage: Database connection configuration
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Location | Administration > Connection Management > Connection Pool Def DB |
| Fields | JDBC URL, Username, Password |
| Usage | Environment-based management of database connection information |
| Dialog Access | By clicking the list icon button to the right of each field |
| Secret Usage | The Password field must be marked as secret |
Usage Scenario: To use different database connection information in different environments
3. LDAP Connection
Usage: LDAP connection configuration
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Location | Administration > Connection Management > Connection Pool Def LDAP |
| Fields | LDAP URL, Bind DN, Bind Password |
| Usage | Environment-based management of LDAP connection information |
| Dialog Access | By clicking the list icon button to the right of each field |
| Secret Usage | Bind Password must be marked as secret |
Senaryo | Problem | Çözüm |
|---|---|---|
Backend API Address Management | Different backend API addresses are used in different environments. |
|
Database Connection Management | Different databases are used in each environment. |
|
API Key Management | Different API keys are used for external services. |
|