Routing Tab - gRPC
If the API type is gRPC, this tab becomes visible.
This section contains routing settings for the gRPC API Proxy Type.
The API Proxy handles messages from the client, applies any policies if available, and then routes the message to the Backend API. The Routing tab is where the settings for how this routing process is performed are configured.
An image containing the Routing Tab settings is provided below:
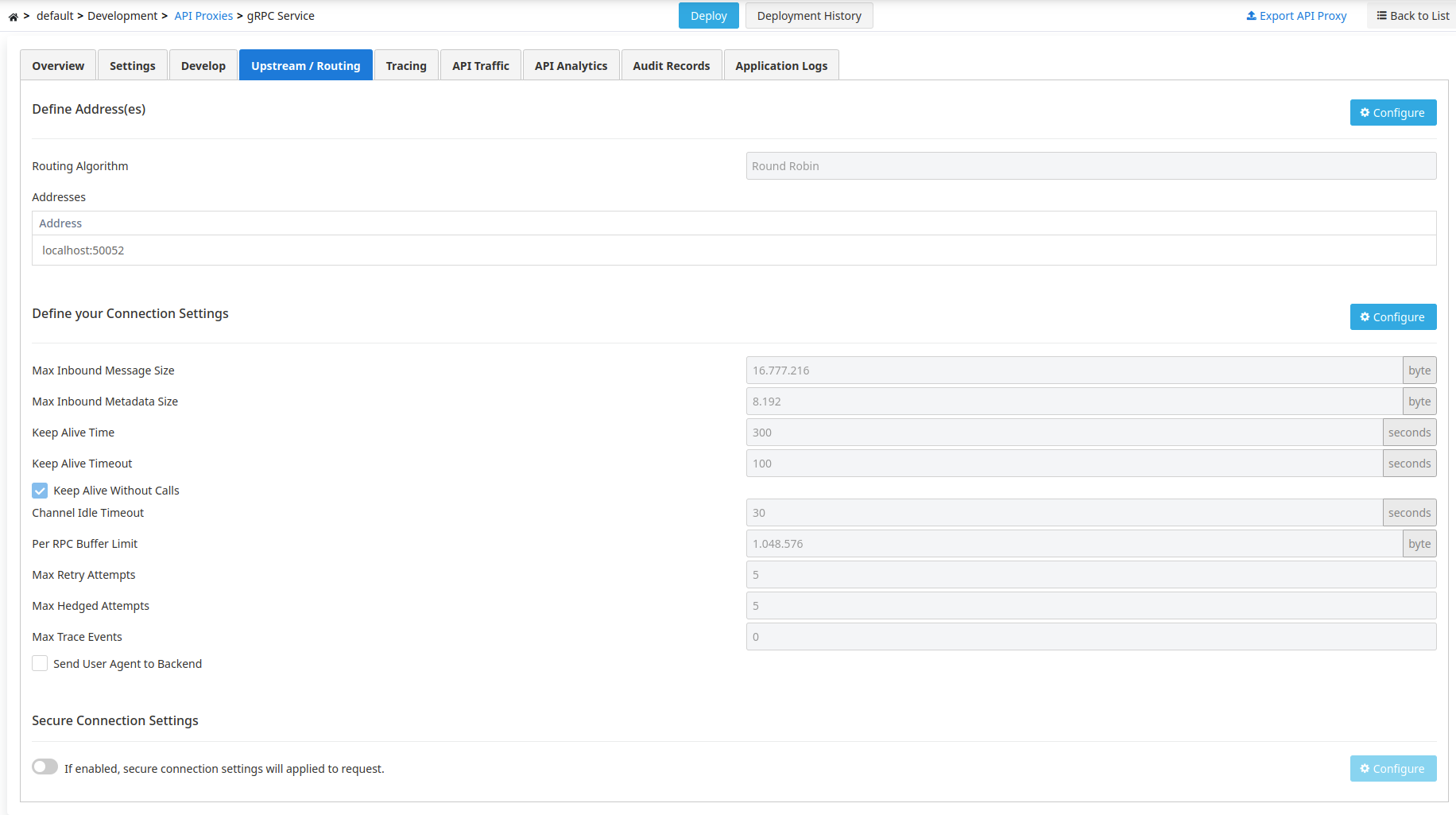
Backend Address Update
When the Configure button in the Address column of the table displaying addresses is clicked, a window opens where the backend address to which the request will be routed can be updated.
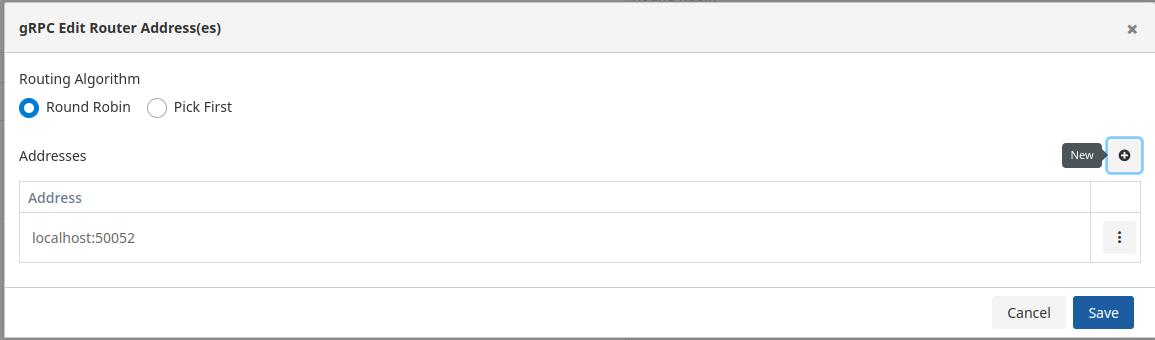
Routing Algorithm
| Algorithm | Description |
|---|---|
| Round Robin | Request messages are sent to the listed addresses in sequence. When the end of the list is reached, it loops back to the beginning, continuing the same cycle. |
| Pick First | Request messages are routed to the first address in the list. |
Adding a New Address
When the Configure button is clicked, a window opens. From this window, clicking the button in the header of the rightmost column opens another window where a new address can be added.
Deleting an Address
To delete an address, select the Remove option from the dropdown menu at the end of the row of the address to be deleted.
At least one address must exist for the API Proxy to perform routing. Therefore, after deleting the last address, the Save button becomes inactive and does not allow saving.
Connection Settings Configuration
The gRPC Connection Settings Definition Tab allows the configuration of connections made via the gRPC protocol. This tab contains various parameters necessary to optimize the performance and security of the connections.
Below is an image containing the details of the settings on this tab:
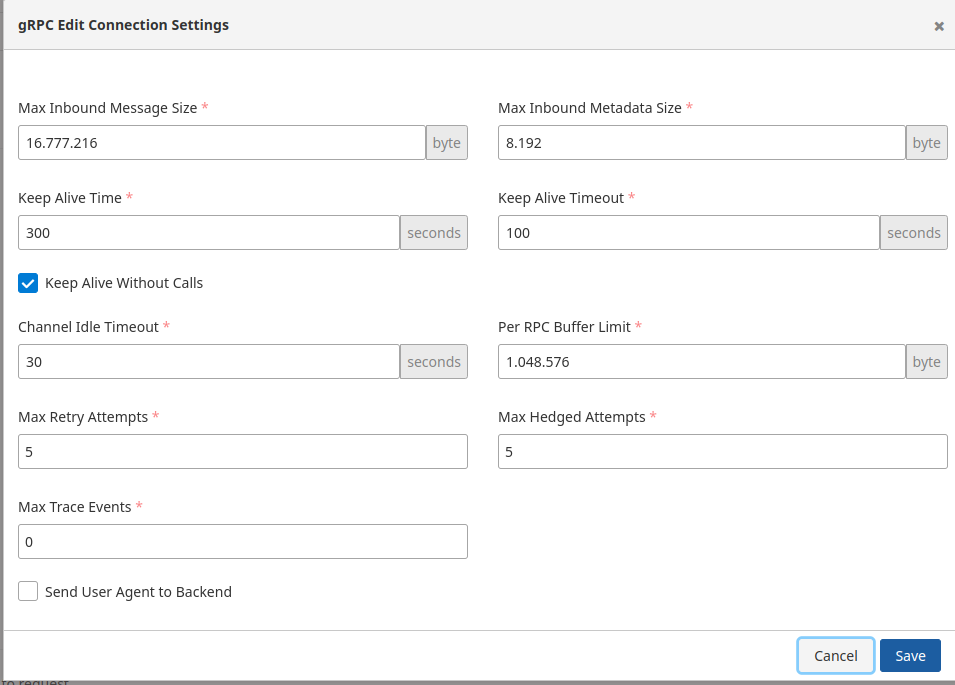
Parameters Used for Connection Settings Configuration
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Max Inbound Message Size | Defines the maximum message size that can be received from the client. |
| Max Inbound Metadata Size | Specifies the maximum metadata size that can be received from the client. |
| Keep Alive Time | Sets the duration for keeping the connection alive. |
| Keep Alive Timeout | Determines the timeout for Keep Alive messages. |
| Keep Alive Without Calls | Configures whether the connection remains alive without active calls. |
| Channel Idle Timeout | Defines the idle time for the channel. |
| Per RPC Buffer Limit | Specifies the buffer memory limit allocated per RPC. |
| Max Retry Attempts | Sets the maximum number of retry attempts. |
| Max Hedged Attempts | Determines the maximum number of attempts when the same request is sent multiple times. |
| Max Trace Events | Defines the maximum number of trace events. |
| Send User Agent to Backend | Indicates whether the User-Agent information will be sent when making a request to the backend. If this option is enabled, the User-Agent value can be customized. |
Secure Connection Setting
When this setting is enabled, selected connection settings are applied to the request.
Thus, the Apinizer client, which will communicate with the target service, verifies the target service's certificate and informs the service that it also has a certificate that should be verified by the target service.
The target service also verifies the client's certificate, establishing secure communication between the client and the target service.
Below is an image containing the configuration settings for the Secure Connection
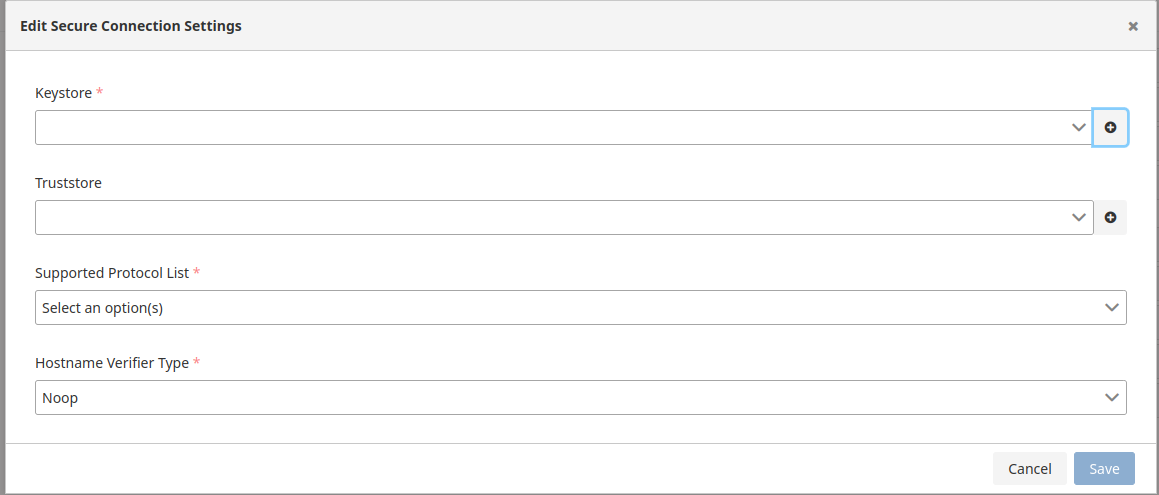
Parameters used for gRPC configuration are shown below.
| Field | Description | |
|---|---|---|
Keystore | Keystore is used to authenticate the client side. Keystore content should include:
| |
| Truststore | Truststore is used to verify the server certificate. The Truststore content must include:
| |
Supported Protocol List | Supported protocols can be selected. Options:
| |
Hostname Verifier Type | The Noop Hostname Verifier disables the hostname verification in SSL/TLS connections, which can be a security risk. It's important to verify the hostname of the server to prevent man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks, where an attacker can intercept the SSL/TLS communication and impersonate the server. Instead of using Noop Hostname Verifier , you can use one of the following hostname verification implementations provided by the Apache HttpComponents client framework:
| |
When gRPC settings are enabled, the existing "http connection pool" in the routing, whose values are specified in the environment settings, is disabled.