Apinizer's Integration with Prometheus and Grafana: A Comprehensive Guide

In today's microservices architecture, monitoring system performance and behavior is vital to maintaining optimal operations. Apinizer, a powerful API management platform, offers robust metrics collection capabilities that can be integrated with industry-standard monitoring tools such as Prometheus and Grafana. This article provides a detailed guide on how you can leverage Apinizer's metrics features to gain valuable insights into your API gateway and cache performance.
Overview of Apinizer's Metric System
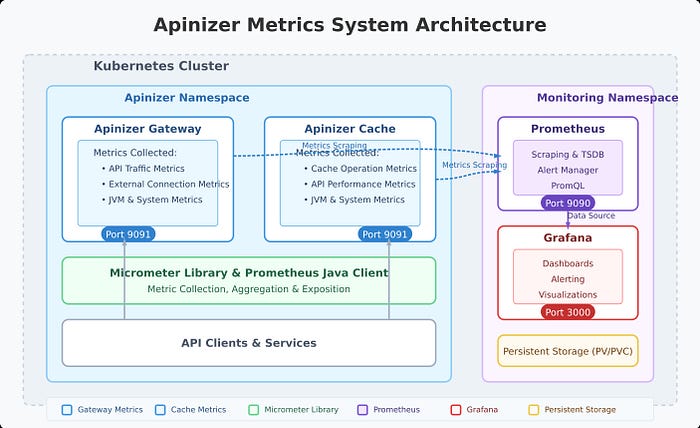
Apinizer's metric system is built on Micrometer. The platform collects a wide range of metrics through two main components:
- Apinizer Gateway: Collects metrics on API traffic, external connections, JVM health and system resources
- Apinizer Cache: Monitors cache operations, API requests, JVM performance and system health
These metrics provide comprehensive visibility into the performance and health of your API management infrastructure, enabling proactive identification of bottlenecks, troubleshooting and capacity planning.
Metrics Collected by Apinizer
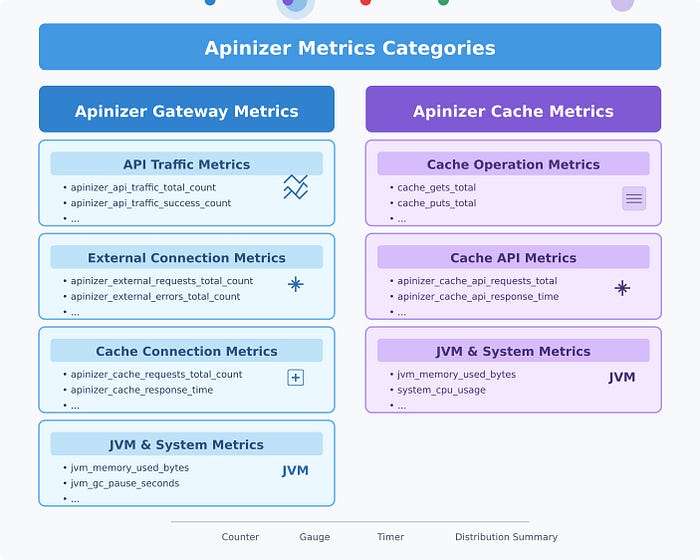
Apinizer Gateway Metrics
The Gateway component collects metrics in various categories:
API Traffic Metrics
These metrics track requests passing through the Apinizer Gateway:
- Total API traffic requests
- Successful/failed/blocked API requests
- Request processing times (pipeline, routing, total)
- Request and response dimensions
- Cache hit statistics
Each metric is available in two forms:
- Total metrics (e.g., total API requests across all APIs)
- Tagged metrics with detailed dimensions (e.g., API ID, requests per API name)
External Connection Metrics
These track connections to external services:
- Total external requests
- Number of external errors
- External response times
JVM Metrics
These provide insights into the Java Virtual Machine:
- Memory usage (heap, non-heap)
- Garbage collection statistics
- Thread counts and states
System Metrics
These monitor the underlying system:
- CPU utilization
- Number of processors
- System load averaging
- File descriptor numbers
Apinizer Cache Metrics
The Cache component collects the following:
Cache Operation Metrics
- Cache get/put counts
- Cache size and number of entries
- Cache operation latencies
- Memory usage by cache entries
API Metrics
- API request numbers
- API response times
- API error counts
JVM and System Metrics
Similar to Gateway, the Cache component monitors JVM performance and system resource utilization.
Setup of Prometheus Integration
1. Enabling Metrics in Apinizer Components
For Apinizer Gateway:
In the Apinizer interface, go to the Gateway Environments page and enable the “Prometheus Metric Server” option. This will enable metric publishing over port 9091.
For Apinizer Cache:
Edit the cache deployment and add the METRICS_ENABLED=TRUE environment variable. This can be done in the following ways:
Through the Apinizer interface: Gateway Environments > Deployments & Services > Cache > Edit deployment
Via Kubernetes CLI:
kubectl edit deploy -n <namespace> cache
# Add the following environment variable
- name: METRICS_ENABLED
value: "true"2. Configuring Prometheus to Collect Metrics
You can configure Prometheus to collect metrics from Apinizer components in two different ways:
Sabit (Constant) Kazıma
Create a service that targets Apinizer components on port 9091:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: cache-prometheus-service # or gateway-prometheus-service
namespace: <NAMESPACE>
spec:
ports:
- port: 9091
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 9091
selector:
app: cache # or worker for Gateway
type: ClusterIPThen configure Prometheus to collect metrics from these services:
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'apinizer-components'
static_configs:
- targets: ['cache-prometheus-service.<NAMESPACE>.svc.cluster.local:9091', 'worker-prometheus-service.<NAMESPACE>.svc.cluster.local:9091']Kubernetes Service Discovery and Dynamic Scraping
For more flexible configurations, you can use Kubernetes service discovery with pod annotations:
1.Add anotations to Deployment:
template:
metadata:
annotations:
prometheus.io/port: "9091"
prometheus.io/scrape: "true"2. Configure Prometheus to use Kubernetes service discovery:
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'kubernetes-pods'
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: pod
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape]
action: keep
regex: true
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_port, __meta_kubernetes_pod_ip]
action: replace
regex: (\d+);((([0-9]+?)(\.|$)){4})
replacement: $2:$1
target_label: __address__
# Additional relabeling configurationsAnalyzing Apinizer Metrics with PromQL
Once you start collecting metrics from Prometheus Apinizer components, you can use PromQL (Prometheus Query Language) to analyze the data. Here are some useful queries:

Gateway API Traffic Analysis
# Total API requests in the last hour
sum(increase(apinizer_api_traffic_total_count_total[1h]))
# Requests per API in the last 5 minutes
sum by (api_name) (increase(apinizer_api_traffic_total_count_tagged_total[5m]))
# API success rate in the last 10 minutes (%)
(sum(increase(apinizer_api_traffic_success_count_total[10m])) / sum(increase(apinizer_api_traffic_total_count_total[10m]))) * 100
# Average response time per API (milliseconds)
sum by (api_name) (rate(apinizer_api_traffic_total_time_tagged_seconds_sum[5m])) / sum by (api_name) (rate(apinizer_api_traffic_total_time_tagged_seconds_count[5m])) * 1000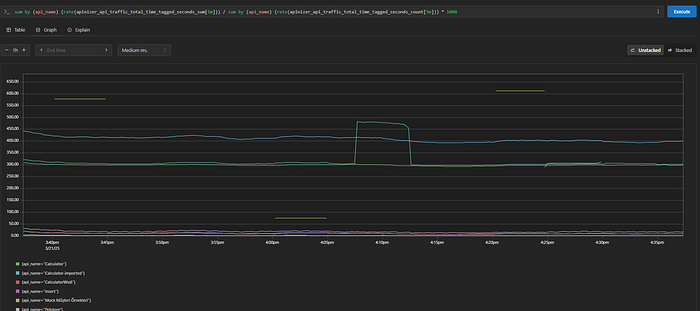
Cache Performance Analysis
# Total cache get operations in the last hour
sum(increase(cache_gets_total[1h]))
# Cache hit rate (%)
(sum(increase(cache_gets_total[5m])) - sum(increase(apinizer_cache_api_errors_total[5m]))) / sum(increase(cache_gets_total[5m])) * 100
# Available cache entries
sum(cache_size)JVM Analysis
# Memory utilization (%)
(sum(jvm_memory_used_bytes{application="apinizer-cache"}) * 100) / sum(jvm_memory_max_bytes{application="apinizer-cache"})
# Garbage collection time
sum(rate(jvm_gc_pause_seconds_sum[5m]))Creating Grafana Dashboards
After setting Prometheus as a data source in Grafana, you can create dashboards to visualize Apinizer metrics. Here are some dashboard suggestions:
API Traffic Dashboard
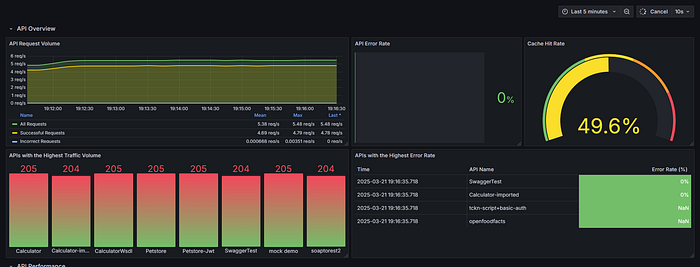
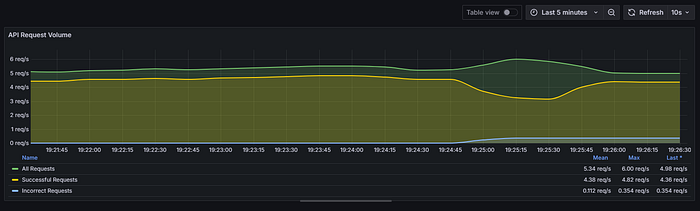
Panel 1: API Request Volume by Type
- Metrics
- Total requests: sum(rate(apinizer_api_traffic_total_count_total[5m]))
- Successful requests: sum(rate(apinizer_api_traffic_success_count_total[5m]))
- Failed requests: sum(rate(apinizer_api_traffic_error_count_total[5m]))
- Visualization Time series
Panel 2: Most Used APIs by Traffic
- Metric:
topk(5, sum by (api_name) (increase(apinizer_api_traffic_total_count_tagged_total[5m]))) - Visualization: Bar chart
Panel 3: API Processing Time Distribution
- Metrics:
- Request pipeline:
sum(rate(apinizer_api_traffic_request_pipeline_time_seconds_sum[5m])) / sum(rate(apinizer_api_traffic_request_pipeline_time_seconds_count[5m])) * 1000 - Routing:
sum(rate(apinizer_api_traffic_routing_time_seconds_sum[5m])) / sum(rate(apinizer_api_traffic_routing_time_seconds_count[5m])) * 1000 - Response pipeline:
sum(rate(apinizer_api_traffic_response_pipeline_time_seconds_sum[5m])) / sum(rate(apinizer_api_traffic_response_pipeline_time_seconds_count[5m])) * 1000 - Visualization: Time series
Panel 4: Request/Response Dimension
- Metrics:
- Request size:
sum(rate(apinizer_api_traffic_request_size_bytes_sum[5m])) / sum(rate(apinizer_api_traffic_request_size_bytes_count[5m])) - Response size:
sum(rate(apinizer_api_traffic_response_size_bytes_sum[5m])) / sum(rate(apinizer_api_traffic_response_size_bytes_count[5m])) - Visualization: Time series
Cache Performance Dashboard
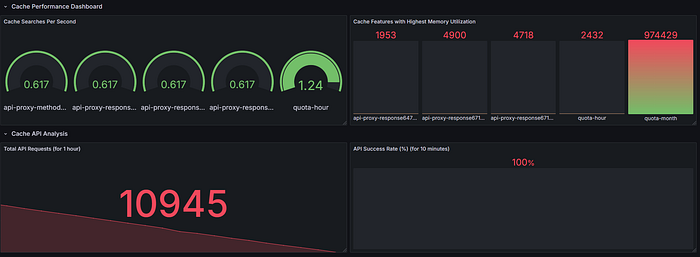
Panel 1: Cache Operations
- Metrics:
- Get operations:
rate(cache_gets_total[5m]) - Put operations:
rate(cache_puts_total[5m]) - Visualization: Time series
Panel 2: Cache Hit Rate
- Metric:
(sum(increase(cache_gets_total[5m])) -sum(increase(apinizer_cache_api_errors_total[5m]))) / sum(increase(cache_gets_total[5m])) * 100 - Visualization: Gauge
Panel 3: Cache Memory Usage
- Metric:
sum(cache_entry_memory_bytes) - Visualization: Statistic or indicator
System Health Dashboard
Panel 1: JVM Memory Usage
- Metric:
sum by (area)(jvm_memory_used_bytes) / sum by (area)(jvm_memory_max_bytes) * 100 - Visualization: Gauge or time series
Panel 2: CPU Utilization
- Metric:
sum(system_cpu_usage{pod=~".*"}) by (pod) * 100 - Visualization: Time series
Panel 3: Active Threads
- Metric:
sum(jvm_threads_live_threads) - Visualization: Statistic or indicator
Best Practices
1. Metric Retention Period
Configure the appropriate retention periods in Prometheus according to your needs. The default configuration retains data for 7 days:
- "--storage.tsdb.path=/prometheus"
- "--storage.tsdb.retention.time=7d"Consider remote storage integrations or adjust these values for longer retention.
2. Alarm Configuration
Set alarms for critical metrics in Prometheus AlertManager or Grafana:
- High API error rates:
(sum(increase(apinizer_api_traffic_error_count_total[5m])) / sum(increase(apinizer_api_traffic_total_count_total[5m]))) * 100 > 10 - High memory usage:
sum(jvm_memory_used_bytes) / sum(jvm_memory_max_bytes) * 100 > 85 - Slow response times:
sum(rate(apinizer_api_traffic_total_time_seconds_sum[5m])) / sum(rate(apinizer_api_traffic_total_time_seconds_count[5m])) > 1
3. Dashboard Organization
Organize your Grafana dashboards logically:
- Create separate dashboards for Gateway and Cache components
- Aggregate relevant metrics
- Use variables that allow filtering by namespace, pod or API
4. Label Usage
Leverage Prometheus tags for more effective querying:
- Filter by specific APIs using the api_name tag
- Analyze metrics by namespace or pod
- Compare performance between different environments
Conclusion
Integrating Apinizer with Prometheus and Grafana provides powerful monitoring capabilities for your API management infrastructure. By properly configuring metric collection, creating informative dashboards, and implementing alarms, you can ensure optimal performance, quickly identify issues, and make data-driven decisions about your API ecosystem.
This integration capitalizes on the strengths of each component:
- Apinizer's comprehensive metrics collection
- Prometheus' efficient time series database and powerful query language
- Grafana's flexible and beautiful visualizations
Start monitoring your Apinizer deployment today to gain deeper insights into API gateway and cache performance.
Sources
For more information: