Development Tab
In this tab, policies, protocol conversion settings and method/endpoint management operations can be done for the selected API Proxy.
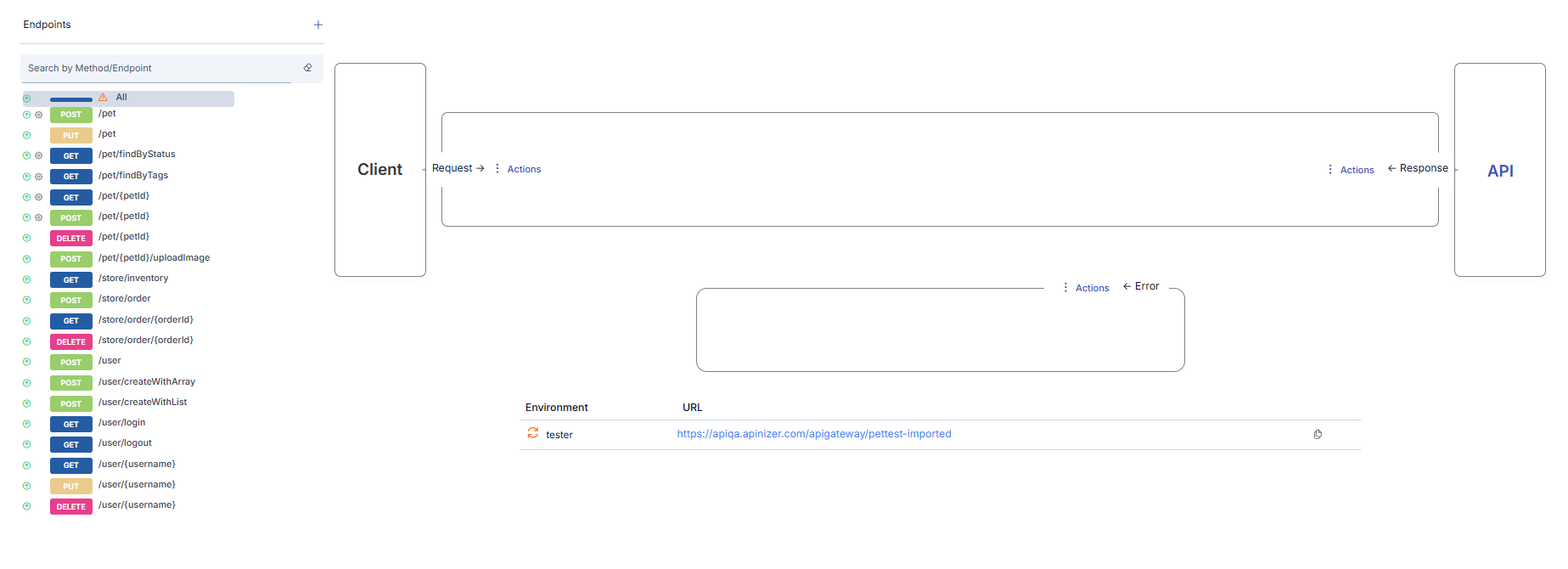
Method/Endpoint Operations
Each API Proxy has its own methods/endpoints that act as a proxy for the methods/endpoints of the Backend API it is created for.
If the API Proxy is created
- using an API Definition File created with the Spec Designer,
- by giving the URL address of the WSDL, Swagger or OpenAPI file, or
- by uploading specification file (WSDL, Swagger or OpenAPI file),
then for each of the existing methods/endpoints in this file, a method/endpoint with the same name is created in the API Proxy automatically.
Users may want to add new methods/endpoints, update existing ones, delete them or disable them for a certain or indefinite period for the following possible reasons:
- One or more new methods/endpoints are added to the Backend API.
- One or more new methods/endpoints are deleted from the Backend API.
- The HTTP method or the name of one or more methods/endpoints in the Backend API are desired to be hidden from the clients.
- One or more methods/endpoints in the backend API are intended to be completely or temporarily closed to clients.
Adding a REST Method/Endpoint
Add button is clicked to add a new method/endpoint.
When the button is clicked, a popup appears where the information of the new method/endpoint to be added can be entered.
REST Endpoint Settings
The picture below shows the endpoint settings of the REST type API Proxy:
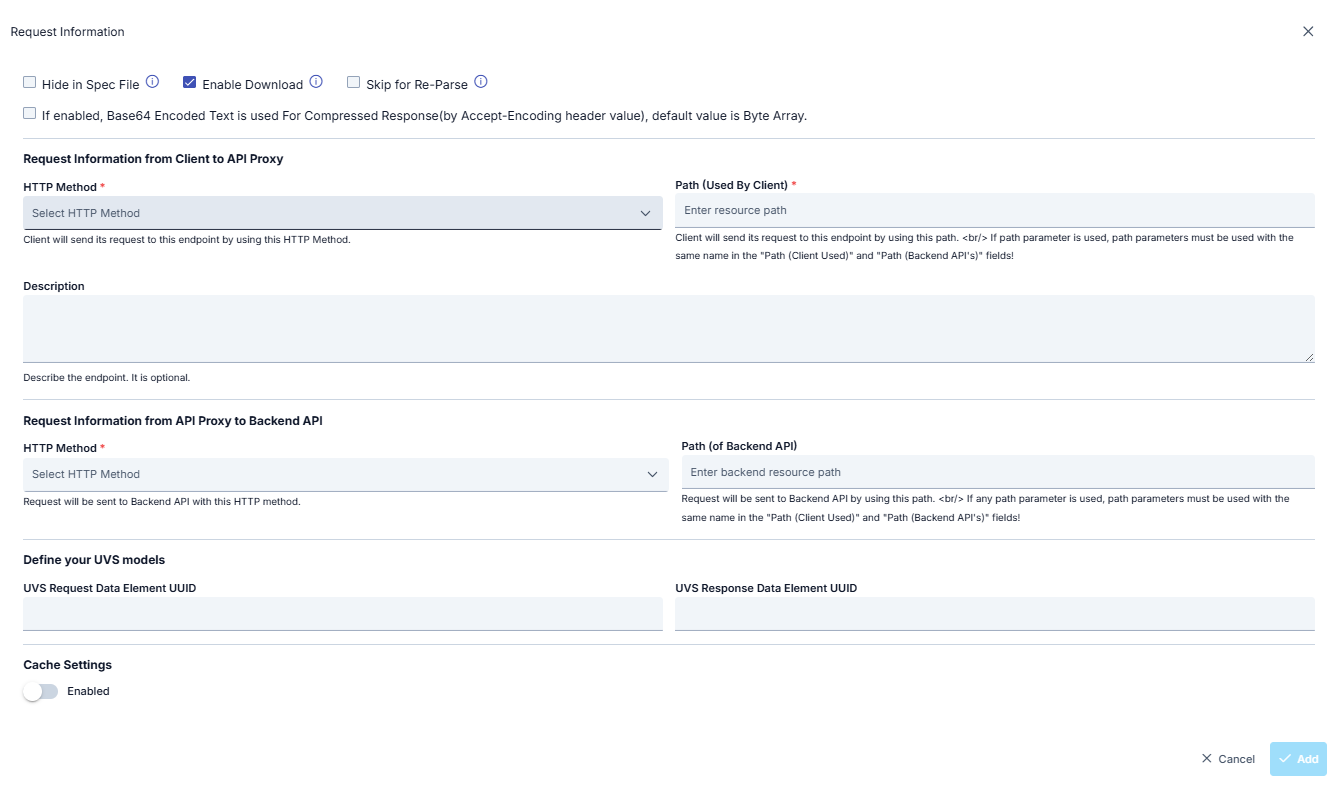
A new method/endpoint is added to the API Proxy when the following information is filled and the Add button is clicked.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Hide in Spec File | If this option is selected, this method will not be shown in Spec File. |
| Enable Download | If the result returned from API Method/Endpoint is of Byte Array type, this option is selected to treat the result as a file. Otherwise, the content is returned to the client as encoded text. In order to decide whether the result is a Byte Array or not, it is checked whether the Content Type Header value is included in the "Byte Array Types" list in the system settings. If it is in this list, it is decided that the result is of Byte Array type. |
| Skip for Re-Parse | When this field is checked, it indicates that this endpoint should not be updated when the API Proxy is re-parsed. For example, even if this endpoint is deleted from the definition file, it will remain intact after the re-parse process. |
| If enabled, Base64 Encoded Text is used For Compressed Response(by Accept-Encoding header value), default value is Byte Array | It is decided whether the response message that will be returned from this method is compressed, by checking whether there are gzip, deflate or br values in the Accept-Encoding value. If one of these values is present, the status of the message is compressed. If the returned message is compressed and the response is of Byte Array type and;
|
HTTP Method (From Client to API Proxy section) | The HTTP method of the method/endpoint. It is mandatory. |
Path (From Client to API Proxy section) | The relative address of the method/endpoint that can be accessed over the URL of the API Proxy. It is mandatory. |
Description (From Client to API Proxy section) | An optional description of the method/endpoint. |
Backend HTTP Method (From API Proxy to Backend API section) | The HTTP method that the method/endpoint of the Backend API expects. It is mandatory. |
Backend Path (From API Proxy to Backend API section) | The relative address of the method/endpoint of the Backend API. It is mandatory. |
Cache Settings | If this option is selected, only HTTP Get requests' responses will be cached. |
Cache Key Type |
|
Variable List | If Create Custom Key is selected as the Cache Key Type, this field becomes active. This list specifies where to retrieve the relevant values in the header, parameter, or body sections of the request message that will be used to generate the cache key. For example; An expression can be written as "Create key based on the APIKEY value in the header of the request message and the XPath value "//identity_no" in the body". |
Capacity | Maximum number of the responses to be cached. |
Invalidation Requires Authn | Selected if authorization is required to invalidate the cache. |
Handling Action | If authorization is required to invalidate the cache, the action to take for unauthorized requests is selected:
|
TTL (seconds) | The length of time the cached response will remain in the cache. It is given in seconds. |
Cache Null Value | Checked if null values are also to be cached. |
SOAP Method Settings
The settings that can be made for the SOAP type API Proxy methods are different from the REST type settings.
It is not possible to add new methods to a SOAP Type API Proxy, only existing methods can be updated.
The picture below shows the method settings of the SOAP type API Proxy:
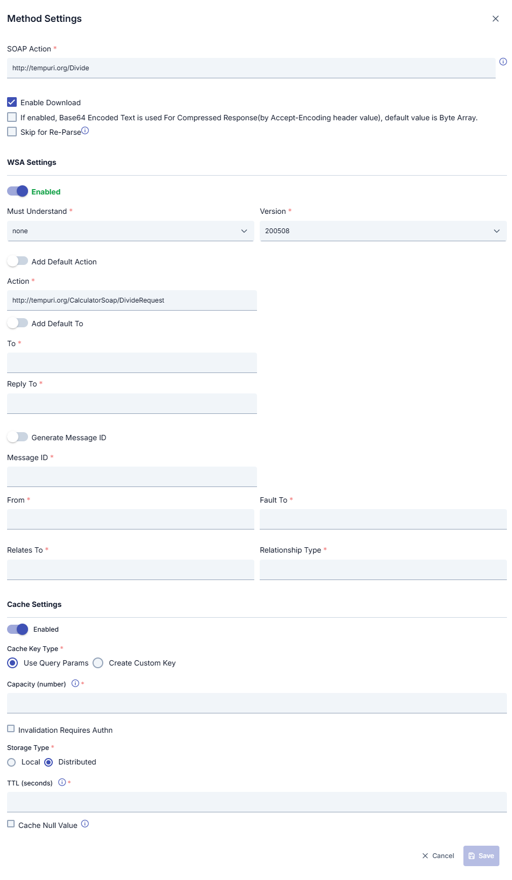
The fields used for the method settings of the SOAP type API Proxy are shown in the table below.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
SOAP Action | When the WSDL file is parsed, the SOAPAction value specified for the method is automatically obtained. However, the value in this field can be changed to use a different value for any reason. |
Enable Download | If the result returned from API Method/Endpoint is of Byte Array type, this option is selected to treat the result as a file. Otherwise, the content is returned to the client as encoded text. In order to decide whether the result is a Byte Array or not, it is checked whether the Content Type Header value is included in the "Byte Array Types" list in the system settings. If it is in this list, it is decided that the result is of Byte Array type. |
| If enabled, Base64 Encoded Text is used For Compressed Response(by Accept-Encoding header value), default value is Byte Array | It is decided whether the response message that will be returned from this method is compressed, by checking whether there are gzip, deflate or br values in the Accept-Encoding value. If one of these values is present, the status of the message is compressed. If the returned message is compressed and the response is of Byte Array type and;
|
Skip for Re-Parse | When this field is checked, it indicates that this method should not be updated when the API Proxy is re-parsed. For example, even if this method is deleted from the definition file, it will remain intact after the re-parse process. |
WSA Settings | With this section, WS-Security Addressing settings can be activated separately for each method. When activated, the corresponding WSA values are added to the SOAP message. |
Must Understand | The "Must Understand" value is set. |
Version | WSA version to be used is selected. |
Add Default Action | It allows the predefined action to be added to the SOAP message when parsing the WSDL file. When activated, the following action statement disappears. |
Action | This field is used to add customized action to the SOAP message. |
Add Default To | It provides the predefined who information to be added to the SOAP message when parsing the WSDL file. When activated, the following to whom statement disappears. |
| To | This field is used to add customized who information to the SOAP message. |
Reply To | This field is used to add customized response to the SOAP message. |
Generate Message ID | This field is activated to add a different generated Message ID for each message to the SOAP message. |
Message ID | This field is activated to add a fixed Message ID for each message to the SOAP message. |
From | This field is used to add customized from information to the SOAP message. |
Fault To | This field is used to add customized error to the SOAP message. |
Relates To | This field is used to add customized error association information to the SOAP message. |
RelationShip Type | This field is used to add customized error relationship type information to the SOAP message. |
Cache Settings | If this setting is activated, method/endpoint based cache settings will be activated. |
Cache Key Type | There are two options for Cache Key Type:
For example, when the query parameter is /methodName?param1=value1¶m2=value2, the key to be kept in the cache consists of the value "param1=value1¶m2=value2"
When this value is selected, a key is created with the fields to be specified in the "Variable List" table |
Variable List | If Create Custom Key is selected as the Cache Key Type, this field becomes active. This list specifies where to retrieve the relevant values in the header, parameter, or body sections of the request message that will be used to generate the cache key. For example; An expression can be written as "Create key based on the APIKEY value in the header of the request message and the XPath value "//identity_no" in the body". |
Capacity | Maximum number of the responses to be cached. |
Invalidation Requires Authn | Selected if authorization is required to invalidate the cache. |
Handling Action | If authorization is required to invalidate the cache, the action to take for unauthorized requests is selected:
|
TTL (seconds) | The length of time the cached response will remain in the cache. It is given in seconds. |
Cache Null Value | Checked if null values are also to be cached. |
Selecting a Method/Endpoint
Clicking the name of any method in the method/endpoint list will select that method and the interface will be updated accordingly.
- The color changes in the list to indicate the selected method/endpoint.
- The selected method/endpoint is displayed in the upper middle section.
- In the lower middle section, the links of the actions that can be taken for this method/endpoint are displayed.
- On the right side, the method/endpoint of the Backend API that the selected method/enpoint is associated with is displayed.
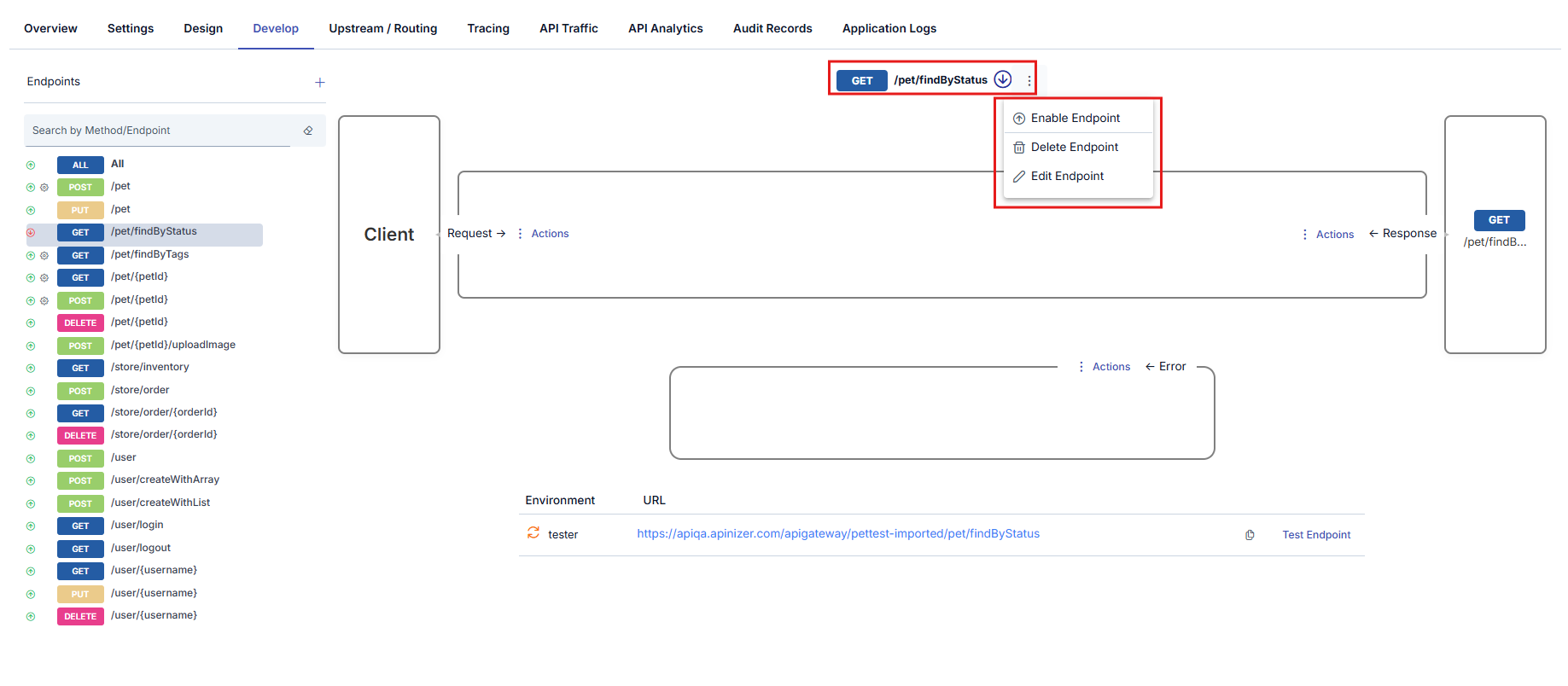
Updating a Method/Endpoint
Edit Endpoint link opens the popup to update the method/endpoint. After entering information, clicking the Save button updates the method/endpoint.
Deleting a Method/Endpoint
Delete Endpoint link is clicked, and the confirmation is given to complete the operation.
Disabling a Method/Endpoint
It is possible to disable a method/endpoint without deleting it.
To do this, click on the Disable Endpoint link. When the link is clicked, the method/endpoint is closed to access and with it, the following changes occur in the interface.
- The icon next to method/endpoint changes to indicate that the method/endpoint is disabled.
- Disable Endpoint link changes to Enable Endpoint.
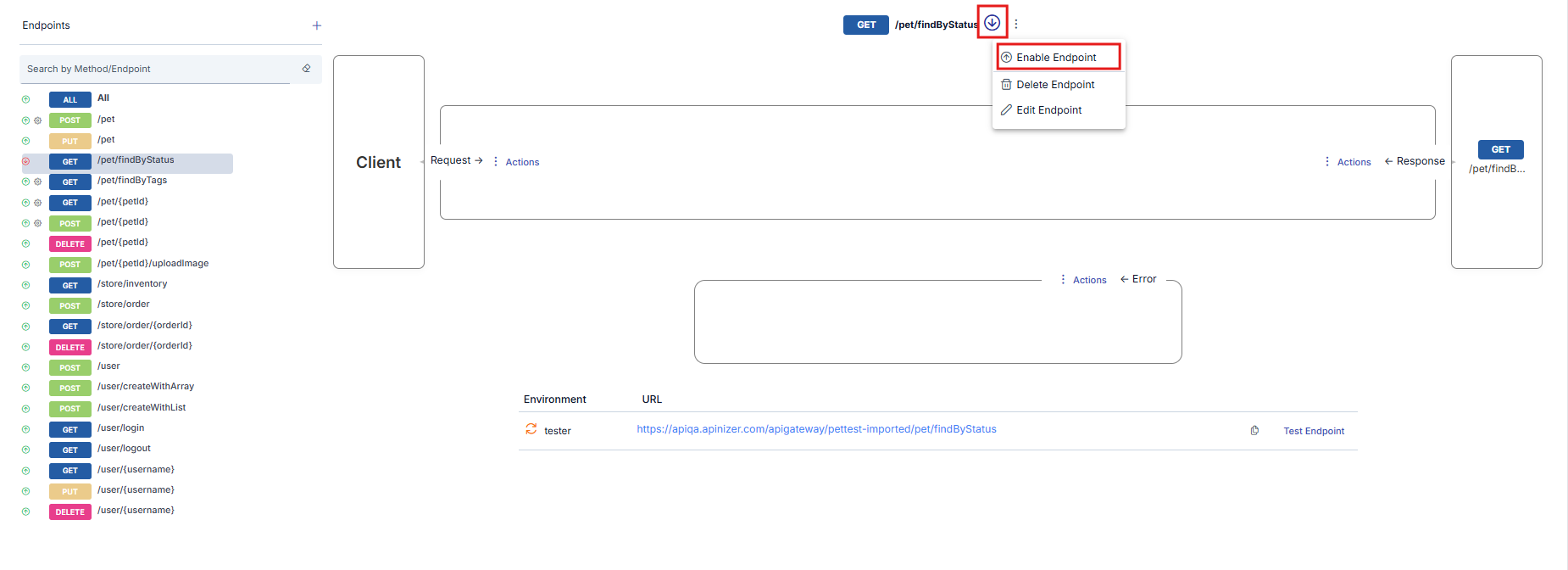
Testing a Method/Endpoint
If an API Proxy is deployed to at least one environment, methods/endpoints can be easily tested within this tab. Clicking the Test Endpoint link for the selected method/endpoint opens the Test Console for this method/endpoint. For detailed information about testing, you can refer to the Test Console interface.